Product Life Cycle - a Strategic View
Function of a Strategy


Product Strategy Over the Life Cycle
The product life-cycle concept suggests that differnet marketing strategies are needed at differnet stages of PLC.The PLC concept also highlights the importance of long-term planning for a new product, including retaliation of competition and its impact on profit and overall ROI at a later stages.
Important point is in PLC concept profit from a product reaches a peak level before sales reaches its peak.Generally growth stage brings profits.In the early part of Maturity stage profits reach peak level then sales approaches its peak.This is due to pricing strategies; enhances service and required to counter competition.

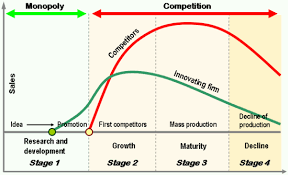
PLC theory in Marketing Strategy




If at all the company decides to eliminate the product / product line then the following factors needs to be considered.


The primary purpose of a strategy is to provide the product manager with the direction to follow in managing business over the planning period. A successful strategy should satisfy three requirements.
Elements of a product strategy
A complete statement of a marketing strategy for a product consist of 7 parts.

- Strategy must help to achieve coordination among various functional areas of the organization.
- Strategy must clearly define how resources are to be allocated.
- Strategy must show hot it can lead to a superior market position
A marketing strategy can be competitively sensible in 4 ways.
- When competitor cannot do it.
- When competitor will choose not to do.
- When competitor would be at a disadvantage if they chose to do it.
- Would cause gain if competitor chose to do it.
A complete statement of a marketing strategy for a product consist of 7 parts.
- A statement of objective(s) the product should attain.
- Selection of strategic alternative(s).
- Selection of customer targets.
- Choice of competitor targets.
- Statement of core strategy
- Description of the supporting market mix.
- Description of the supporting functional program.



Product Strategy Over the Life Cycle
The product life-cycle concept suggests that differnet marketing strategies are needed at differnet stages of PLC.The PLC concept also highlights the importance of long-term planning for a new product, including retaliation of competition and its impact on profit and overall ROI at a later stages.
Important point is in PLC concept profit from a product reaches a peak level before sales reaches its peak.Generally growth stage brings profits.In the early part of Maturity stage profits reach peak level then sales approaches its peak.This is due to pricing strategies; enhances service and required to counter competition.

PLC theory in Marketing Strategy
- Introduction Stage: The acceptance of a new industrial product during introduction stage would depend on the customer's acceptance inertia. This by and large depends on the value that customer would attach to the product in solving his problem.
- Core Strategy at this stage
- Skimming:
- Product feature based differential advantage allows high price
- Market Segment : Pioneer or Early Adopters.
- Price sensitivity: Insensitive
- Useful when cost structure of product is largely variable cost not under pressure to cover large fixed costs.
- Strategy successful when high entry barrier exists.
- Penetration
- Low price core strategy
- Market Segment: Wider segment pursued.
- Efforts to gain market share as quickly as possible.
- Involves generic or product category marketing and spend heavily on trade oriented promotions.
- Strategy is used when the lead in the market will likely be short-lived.
- Growth Stage: The growth phase of the PLC actually encompasses 2 different kinds of market behaviour.
- Early Growth - the phase just following the introductory phase
- Late Growth - the phase in which the rapid increase in sales begin to flatten out.
- Features of the growth phase
- The number of competitors are growing
- Customers becomes knowledgeable about product and availability leading to pressure on price.
- Increase competition forces market segmentation becomes the key focus.
- The strategic option followed by either a leader or a follower are are as follows


- During the growth stage an industrial marketeer focuses on the below 3 key areas.
- Improve product design; -> pack more value / benefit; Segment stretch
- Improve distribution; -> reach out to segment faster by facilitating product accessibility.
- Reduce price and gain more volume.-> Improve economy of scale.
- Maturity Stage: At this stage one needs to also review strategy using Ansoff matrix. In order to counter the competition and the consequent decline in profits the 3 steps that could be taken are as below.
- Enter new market / Segment / customers.
- Keep the existing customer satisfied (improve service).
- Cut internal cost to maintain the profits.-> reduce marketing, production, and other cost;

- Decline Stage: Either one should withdraw the product or develop a substitute. In Industrial marketing framework the decline is very rapid and this stage is shorter.
- Product Evaluation Matrix: Evaluate the performance of all the existing products / product lines using this technique.
- Perceptual Mapping Technique: Examine the relative strength and weakness of company's product in comparison to competitors.
- Based on the above 2 analysis decide product strategy:
- Whether to continue
- Whether to modify
- Whether to eliminate or drop the product.
- Whether to add new product or product line.

Product Elimination
- Will the customer relationship be affected?
- Will the profitability be affected due to change in overhead (fixed cost) allocation ?
- What will be the reaction of the employee?
- Will the sales of other products be affected?
- Is there a new product to replace the eliminated product?
- Will the company's image be affected?
- What will be the possible competitive reaction?
- Exporting Product: Exporting a successful product at home to a foreign country.
- Localization in Foreign land: The parent country forms JV or partner or set up own base.
- Cost optimization: Take advantage of lower input & labor cost becomes more effective.
- Start importing back into home country: Internal competition. Pressure to develop new generation products.
Locating Industrial Products on the PLC curve
PLC of a particular industrial product would depend on factors like
- Industry profits (as % of sales)
- Rate of change in industry sales growth
- Information about competitors
The steps involved in locating a product in PLC are as follows.
- Develop a trend analysis.for the past 3-5 years
- Competitor analysis for market share; product performance; NPI; diversification or expansion plans
- Forecast sales / profit over 3-5 years
- From the above 3 steps fix a product's position in PLC curve.

Porter 5-force analysis is also very handy is making a new product launch decision.

Nice
ReplyDeleteFantastic blog! The insights on book publishing were spot on and super helpful. If you're looking to turn your manuscript into a masterpiece, Ottenheimer Publishers is the go-to name. With a legacy of excellence and a passion for storytelling, we help authors bring their visions to life. From editing to global distribution, we've got it all covered. Your publishing journey deserves nothing less than Ottenheimer precision!
ReplyDelete